How to Choose a Centrifugal Pump: A Practical Guide from an Industry Expert
By Bijan, Founder & Lead Engineer at Spring Pump
With over two decades in the industrial pump industry, I’ve helped thousands of engineers, plant managers, and contractors navigate the complex process of selecting the right equipment. The most common question I get is, “How do I choose a centrifugal pump?”
Choosing the wrong pump is costly. It leads to premature failure, excessive energy consumption, and costly downtime. The secret to getting it right isn’t a mystery—it’s a methodical process based on your application’s specific requirements.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through the exact steps and critical factors my team and I use at Spring Pump to ensure our clients select a pump that is reliable, efficient, and perfectly matched to the job. Let’s dive in.
The 5 Non-Negotiables of Centrifugal Pump Selection
Before you even look at a pump model or a brand, you need a clear understanding of these five application parameters. Getting these right is 90% of the battle.
1. Define Your Flow Rate (GPM)
What it is: Flow Rate, measured in Gallons Per Minute (GPM), is the volume of liquid you need the pump to move within a specific time frame.
How to determine it: This is often a process requirement. Is your system designed to fill a 500-gallon tank in 10 minutes? That’s a 50 GPM requirement. Understand your system’s maximum, minimum, and average flow needs.
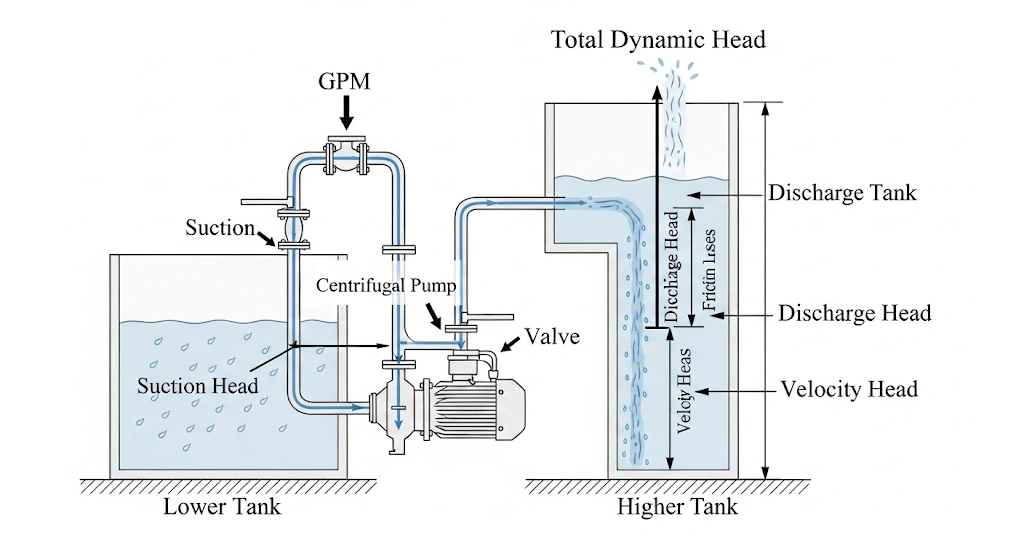
2. Calculate Your Total Dynamic Head (TDH)
What it is: Total Dynamic Head (TDH) is the total pressure the pump must overcome to move the liquid. It is the single most important factor in pump selection and is measured in feet. It is NOT just vertical lift. TDH is the sum of:
- Static Head: The vertical height the liquid must be lifted.
- Friction Head: The pressure loss due to friction as the liquid moves through pipes, valves, and fittings.
- Pressure Head: The difference in pressure between the suction and discharge tanks.
A common mistake: Confusing head with pressure. Remember: pump curves are in feet of head, not PSI. You must calculate the total system resistance.
3. Understand Your Fluid Properties
The liquid you’re pumping defines the pump’s construction materials and type.
- Specific Gravity: The weight of the fluid compared to water. This directly affects the horsepower required. A higher specific gravity fluid requires more power to pump.
- Viscosity: The thickness or resistance to flow of a fluid. Standard centrifugal pumps are excellent for thin, water-like fluids (low viscosity). High-viscosity fluids (like oil, syrup, or sludge) require special pump designs or larger pumps to overcome the internal resistance.
- Temperature, Abrasiveness, and Corrosiveness: Is the fluid hot, acidic, or contain suspended solids? This determines whether you need a pump made of stainless steel, cast iron, or other specialized alloys. For a deeper dive into how pumps handle different fluids, understanding Centrifugal Pump Parts & Functions is crucial.
4. Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH): Avoiding Cavitation
This is the most technical but critical concept. NPSH ensures your pump doesn’t cavitate.
- NPSH Available (NPSHa): This is a property of your specific system layout. It’s the absolute pressure at the pump’s suction flange.
- NPSH Required (NPSHr): This is a property of the pump itself, found on its curve. It’s the minimum pressure required at the suction port to prevent cavitation.
The Golden Rule: NPSHa must be greater than NPSHr. Always have a safety margin of at least 1.5 feet or more. If NPSHa is too low, the pump will cavitate—a destructive process that sounds like pumping gravel and quickly destroys impellers and seals.
5. Matching the Pump to the Duty Point
Once you have your GPM and TDH, you plot this on a pump performance curve. Your ideal “duty point” (where GPM and TDH meet) should be as close as possible to the pump’s Best Efficiency Point (BEP). Operating near the BEP ensures longer life, lower energy costs, and less vibration and noise.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How do I choose the right size pump?
The “right size” is determined by accurately calculating your Flow Rate (GPM) and Total Dynamic Head (TDH). These two numbers will point you to a specific pump model and impeller size on a manufacturer’s performance curve. It’s not about physical size, but about performance capability.
What factors should be considered when selecting a pump?
Beyond the core five (GPM, TDH, Fluid, NPSH, Duty Point), consider:
- Power Source: Is electric, diesel, or pneumatic power available?
- Environment: Is the pump for a hazardous, corrosive, or clean environment?
- Regulations: Are there specific industry standards to meet (e.g., FDA, API)?
- Total Cost of Ownership: Consider initial purchase price, expected maintenance, spare parts cost, and energy efficiency.
What is GPM and head in a pump?
GPM (Gallons Per Minute) is the pump’s flow rate capacity—how much liquid it can move.
Head (in feet) is the pump’s pressure capability—how far and against what resistance it can move that liquid. They are inversely related on a pump curve: as flow increases, head decreases, and vice versa.
How do you determine pump requirements?
- Define the Application: What is the pump’s job? (e.g., transfer, circulation, pressure boosting).
- Gather System Data: Calculate required GPM and TDH.
- Analyze the Fluid: Identify all fluid properties (specific gravity, viscosity, etc.).
- Check Suction Conditions: Calculate NPSHa to ensure it is sufficient.
- Review the Environment and Other Constraints.
Conclusion: Your Blueprint for Success
Selecting a centrifugal pump doesn’t have to be a gamble. By systematically working through your flow rate, total dynamic head, fluid properties, and NPSH requirements, you can make a data-driven decision that ensures reliability and efficiency for years to come.
At Spring Pump, we’ve built our business on helping professionals like you navigate this process. We don’t just sell pumps; we provide solutions.
Ready to Find Your Perfect Pump?
You don’t have to figure this out alone. Use our expert knowledge to your advantage.
Browse our extensive inventory of high-performance Centrifugal Pumps to see our range of solutions. Then, contact our technical team today. Provide us with your application details, and let us do the heavy lifting. We’ll perform the calculations and recommend the ideal pump for your specific needs, ensuring you get it right the first time.
>> Explore Our Centrifugal Pumps Collection Here <<
